What is a Tensor?
3 # a rank 0 tensor; this is a scalar with shape []
[1. ,2., 3.] # a rank 1 tensor; this is a vector with shape [3]
[[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]] # a rank 2 tensor; a matrix with shape [2, 3]
[[[1., 2., 3.]], [[7., 8., 9.]]] # a rank 3 tensor with shape [2, 1, 3]
How to use Tensorflow?
Create graphs and run them
import tensorflow as tf
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32)
node2 = tf.constant(4.0) # also tf.float32 implicitly
sess = tf.Session() #Create a session
node3 = tf.add(node1, node2) #Create operations
print("sess.run(node3): ",sess.run(node3)) #Run graph
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
A placeholder is a promise to provide a value later.
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_node = a + b # + provides a shortcut for tf.add(a, b)
print(sess.run(adder_node, {a: 3, b:4.5}))
print(sess.run(adder_node, {a: [1,3], b: [2, 4]}))
(We can make the computational graph more complex by adding another operation.)
add_and_triple = adder_node * 3.
print(sess.run(add_and_triple, {a: 3, b:4.5}))
Create Variables to be able to Train
Variables allow us to add trainable parameters to a graph. They are constructed with a type and initial value:
W = tf.Variable([.3], tf.float32)
b = tf.Variable([-.3], tf.float32)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
linear_model = W * x + b
# Need to explicitly initialize with default values
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()sess.run(init)
#Just runs the linear model to produce outputs with default W and b values
print(sess.run(linear_model, {x:[1,2,3,4]}))
#You can change W and B by the following code:
fixW = tf.assign(W, [-1.])
fixb = tf.assign(b, [1.])
sess.run([fixW, fixb]) #changed W and B
print(sess.run(linear_model, {x:[1,2,3,4]}))
Create Loss
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# loss
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(linear_model - y)) # sum of the squares
# optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# training data
x_train = [1,2,3,4]
y_train = [0,-1,-2,-3]
# training loop
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init) # reset values to wrong
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train, {x:x_train, y:y_train}) #This changes W and b as they are Variables
Now to check the vales of W and B we can do a sess.run
sess.run(W) #array([-0.9999904], dtype=float32)
sess.run(b) #array([ 0.99997181], dtype=float32)
final_loss = sess.run(loss, {x:x_train, y:y_train}) #loss: 5.69997e-11
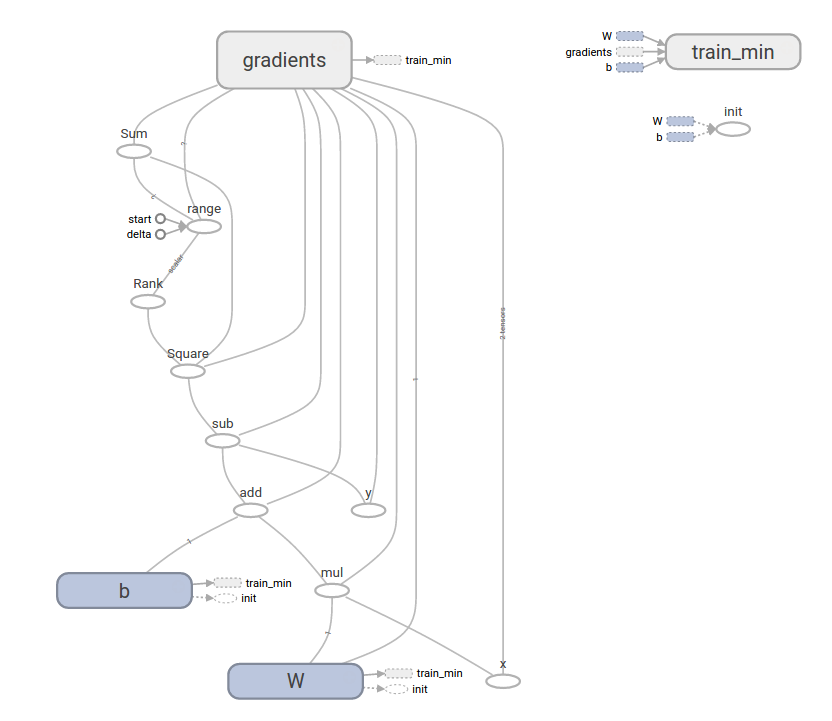
This more complicated program can still be visualized in TensorBoard